Surface water protection
Most of our human activities leave traces in the water (traffic, medicine, industry, human waste etc).
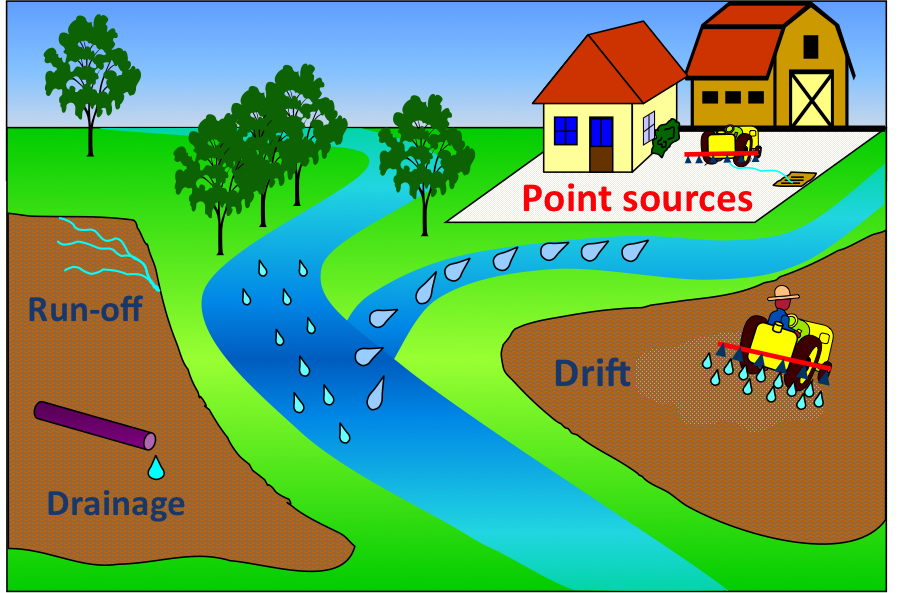
Agricultural activities contribute to water pollution through entries of plant nutrients (mainly Nitrogen and Phosphate) and Plant Protection Products (PPP). Entry routes of PPP to surface water are
· Point sources
Point sources originate mainly from the farmyard and can be seen as a result of incorrect use and the use of not fully environmentally optimized equipment and infrastructure. Point sources are considered the main entry route contributing more than 50%.
Point sources PPP pollution is mainly measured at the outlet of sewage plants, which connect different farmyards to the local sewage system. Findings are compared with those measured in a water body carrying PPP traces from a catchment area.
Specific to point source pollution is that all relevant factors to prevent such pollution can be managed if the handling of PPP follows the BMPs.
Each user of a sprayer is a target for BMPs information and potential pollution risks are not related to the size of a farm.
Agricultural activities contribute to water pollution through entries of plant nutrients (mainly Nitrogen and Phosphate) and Plant Protection Products (PPP). Entry routes of PPP to surface water are
· Point sources
Point sources originate mainly from the farmyard and can be seen as a result of incorrect use and the use of not fully environmentally optimized equipment and infrastructure. Point sources are considered the main entry route contributing more than 50%.
Point sources PPP pollution is mainly measured at the outlet of sewage plants, which connect different farmyards to the local sewage system. Findings are compared with those measured in a water body carrying PPP traces from a catchment area.
Specific to point source pollution is that all relevant factors to prevent such pollution can be managed if the handling of PPP follows the BMPs.
Each user of a sprayer is a target for BMPs information and potential pollution risks are not related to the size of a farm.
· Diffuse sources
Main diffuse source entry routes are runoff / erosion, spray drift and entries from drainage discharge.
· Runoff / erosion
Runoff is considered the main diffuse source entry route contributing about 30 to 35% to the PPP surface water pollution. Runoff and erosion is a natural process influenced mainly by the weather conditions (intensive rain), soil characteristics and the landscape. Agriculture influences the runoff risk through soil tillage practices, cropping pattern, size of fields and others.
· Spray drift
Spray drift is the transfer of spray droplets out of the target area by wind. Spray drift reduction is not only related to water but also to adjacent housing areas and bystanders. Spray drift for water pollution is less significant for field applications but more important for applications in orchards and vine crops (1 to 5%).
· Drainage
Drainage systems are installed to prevent water saturation of the topsoil. Runoff which would be normal in such fields is controlled by the drainage system. Drainage systems can be a source of PPP entry during the time if the drains flow. This is usually in winter and early spring when plants are consuming little water or the soil is bare. Another situation supporting PPP entries via the drainage system can be in dry periods when the soil is dry and cracking. Heavy rains in this situation can wash PPP through the cracks into the drainage.
Main diffuse source entry routes are runoff / erosion, spray drift and entries from drainage discharge.
· Runoff / erosion
Runoff is considered the main diffuse source entry route contributing about 30 to 35% to the PPP surface water pollution. Runoff and erosion is a natural process influenced mainly by the weather conditions (intensive rain), soil characteristics and the landscape. Agriculture influences the runoff risk through soil tillage practices, cropping pattern, size of fields and others.
· Spray drift
Spray drift is the transfer of spray droplets out of the target area by wind. Spray drift reduction is not only related to water but also to adjacent housing areas and bystanders. Spray drift for water pollution is less significant for field applications but more important for applications in orchards and vine crops (1 to 5%).
· Drainage
Drainage systems are installed to prevent water saturation of the topsoil. Runoff which would be normal in such fields is controlled by the drainage system. Drainage systems can be a source of PPP entry during the time if the drains flow. This is usually in winter and early spring when plants are consuming little water or the soil is bare. Another situation supporting PPP entries via the drainage system can be in dry periods when the soil is dry and cracking. Heavy rains in this situation can wash PPP through the cracks into the drainage.
Questions? Contact our project manager!
|
This project is part of the European crop protection industry’s commitment to contributing towards high quality affordable food, safeguarding water, promoting biodiversity, and protecting health. Discover more at www.hungry4change.eu
|