Nearly all human activities release traces in the water:
· Fertilizers and Pesticides (PPP)
· Human and animal waste
· Plastics and heavy metals
· Other manmade and natural chemicals
Concerning water protection and pesticides regulations in the EU are very strict and are based on the hazard principle.* The drinking water threshold value for PPP is set at 0,1 µg/l , which is practically a zero tolerance. It takes a water course 30 cm deep, 1 meter wide and 33 km long to dilute 1 g active ingredient to the drinking water threshold.
· Fertilizers and Pesticides (PPP)
· Human and animal waste
· Plastics and heavy metals
· Other manmade and natural chemicals
Concerning water protection and pesticides regulations in the EU are very strict and are based on the hazard principle.* The drinking water threshold value for PPP is set at 0,1 µg/l , which is practically a zero tolerance. It takes a water course 30 cm deep, 1 meter wide and 33 km long to dilute 1 g active ingredient to the drinking water threshold.
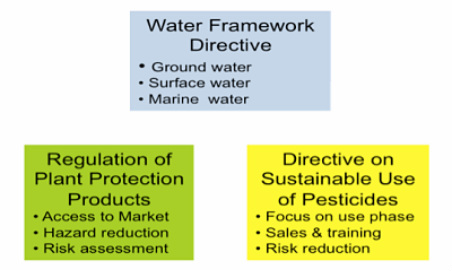
Key regulations to protect water from losses to water are the Water Framework Directive (WFD), which aims to develop all waters surface, ground and marine waters to a good chemical and ecological status by 2015. The Plant Protection Products regulation, which regulate the access to the market and most recently the Directive on sustainable use of pesticides, which focus on the use phase of the PPP. This directive requires from the EU member states to establish regular trainings for operators to support the correct use of the products and to establish mandatory testing of sprayers.
*Hazard principle: The situation has the potential to be hazardous, but no people, property, or environment is currently affected by this.
Questions? Contact our project manager!
|
This project is part of the European crop protection industry’s commitment to contributing towards high quality affordable food, safeguarding water, promoting biodiversity, and protecting health. Discover more at www.hungry4change.eu
|