If sensitive areas (housing area, water course, sensitive crops, area for biodiversity) are adjacent to the treated field, special attention is required in relation to treatment planning, spray technologies used and calibration and an adapted management of the application is necessary.
Minimum dDistance regulations for spraying PPP near to sensitive areas are usually listed on the PPP labels and need to be respected. Depending on the legal situation in countries, official recommendations concerning distance regulations can be modified by the use of spray drift reducing technologies.
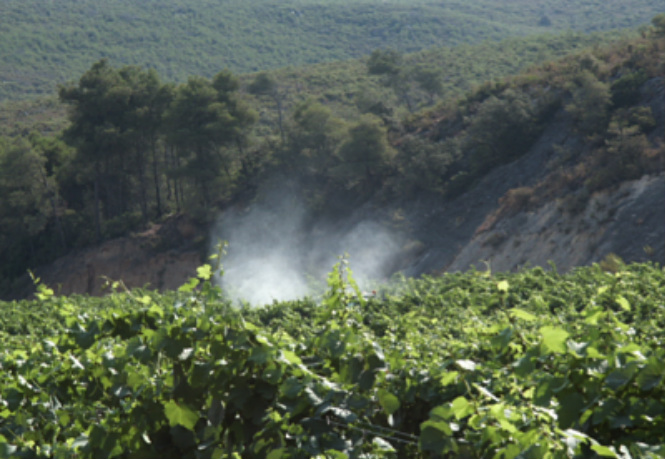
Contrary to wide spread perceptions, spray drift is a rather minor entry route into surface water compared to other routes but can be more important for . Applications in vine and orchard crops are more critical concerning spray drift than in field crops due to type of sprayers used and the orientation of spray droplets.
In orchard and vine application the spray droplet are transported to the target by air support. The spray direction is mainly upwards and to the side of the crop rows. Field applications are generally directed downwards and droplets are less exposed to wind transfer or turbulences.
Minimum dDistance regulations for spraying PPP near to sensitive areas are usually listed on the PPP labels and need to be respected. Depending on the legal situation in countries, official recommendations concerning distance regulations can be modified by the use of spray drift reducing technologies.
Contrary to wide spread perceptions, spray drift is a rather minor entry route into surface water compared to other routes but can be more important for . Applications in vine and orchard crops are more critical concerning spray drift than in field crops due to type of sprayers used and the orientation of spray droplets.
In orchard and vine application the spray droplet are transported to the target by air support. The spray direction is mainly upwards and to the side of the crop rows. Field applications are generally directed downwards and droplets are less exposed to wind transfer or turbulences.
Key influencing factors for spray drift
How these factors work and how they are interacting can be learned by using the TOPPS online drift evaluation tool (available in 8 languages) in the tools section.
How these factors work and how they are interacting can be learned by using the TOPPS online drift evaluation tool (available in 8 languages) in the tools section.
How these factors work and how they are interacting can be learned by using the TOPPS online drift evaluation tool (available in 8 languages) in the tools section.
Mitigation measures
 Picture: DLZ-Rheinland-Pfalz, Neustadt
Picture: DLZ-Rheinland-Pfalz, Neustadt
Orchard/vine
Droplet generation
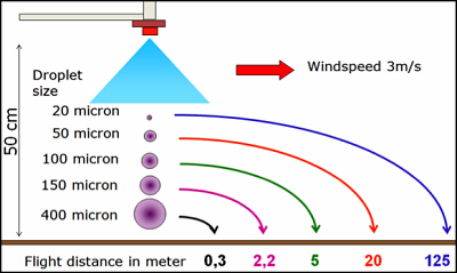
Hydraulic nozzles offer a wide option for modifying droplet spectra.
Some countries classify nozzles on their drift reducing potential
Other dispersion principles like pneumatic dispersion are less flexible in adjusting droplet spectra.
Droplet generation
Hydraulic nozzles offer a wide option for modifying droplet spectra.
Some countries classify nozzles on their drift reducing potential
Other dispersion principles like pneumatic dispersion are less flexible in adjusting droplet spectra.
 Picture: DLZ-Rheinland-Pfalz, Neustadt
Picture: DLZ-Rheinland-Pfalz, Neustadt
Correct adjustment of sprayer forto the cropheight and canopy density of the crop is important
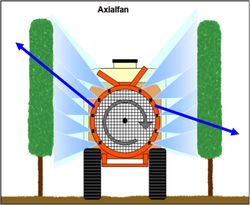
· Adapt air volume & direction
· Adapt air stream to the correct height of the crop with windshields
· Consider the asymmetric air stream
Often more air is used than necessary.
· Adapt air volume & direction
· Adapt air stream to the correct height of the crop with windshields
· Consider the asymmetric air stream
Often more air is used than necessary.
Spray scenario in case spraying cannot be postponed or sudden change of wind direction
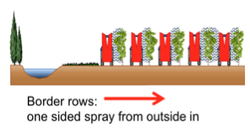
· Spray border rows from outside in from one side (against the wind)
· Reduce or shut air support
· Spray border rows from outside in from one side (against the wind)
· Reduce or shut air support
Field applications

· Use spray drift reducing nozzles
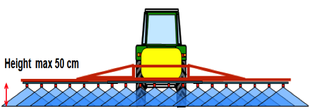
· Keep the spray boom as low as possible not higher than 50 cm
· Spraying along sensitive areas: Take extra care and do not drive faster than than 8 km/h
· Keep the spray boom as low as possible not higher than 50 cm
· Spraying along sensitive areas: Take extra care and do not drive faster than than 8 km/h
|
This project is part of the European crop protection industry’s commitment to contributing towards high quality affordable food, safeguarding water, promoting biodiversity, and protecting health. Discover more at www.hungry4change.eu
|