Reduction of Runoff and Erosion
Runoff / erosion processes result in the transfer of water / soil from fields to adjacent land / water courses. These processes also transfer plant nutrients (Nitrogen, Phosphorus) and pesticides (PPPs). Pesticide runoff represents the most important diffuse source entry route of PPP into surface water. Entries of PPP cannot be completely avoided from runoff / erosion, but can be significantly reduced with appropriate mitigation measures to acceptable levels.
Runoff / erosion processes result in the transfer of water / soil from fields to adjacent land / water courses. These processes also transfer plant nutrients (Nitrogen, Phosphorus) and pesticides (PPPs). Pesticide runoff represents the most important diffuse source entry route of PPP into surface water. Entries of PPP cannot be completely avoided from runoff / erosion, but can be significantly reduced with appropriate mitigation measures to acceptable levels.

Factors affecting runoff are:
· Volume and intensity of rain events
· Type and properties of the soil
· Landscape factors, e.g. slopes
· Soil and crop management practices, plus land use patterns
· Volume and intensity of rain events
· Type and properties of the soil
· Landscape factors, e.g. slopes
· Soil and crop management practices, plus land use patterns
Three different types of runoff
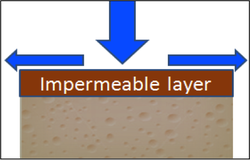
Runoff - surface infiltration restriction
· Capped soils impair the infiltration of water, particularly silty soils;
· Soils often cap early in the season when fields are relatively bare;
· Rainfall intensity is important, as caps act like a "bottle neck" to flow.
· Capped soils impair the infiltration of water, particularly silty soils;
· Soils often cap early in the season when fields are relatively bare;
· Rainfall intensity is important, as caps act like a "bottle neck" to flow.
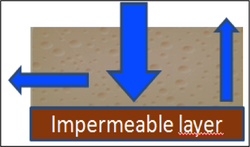
Runoff - subsurface drainage restriction
· The soil infiltration capacity decreases with subsurface drainage restrictions, e.g. compacted layers of heavy subsoil.
· The capacity is mainly exceeded in winter with high rainfall/low evapo-transpiration.
· The soil infiltration capacity decreases with subsurface drainage restrictions, e.g. compacted layers of heavy subsoil.
· The capacity is mainly exceeded in winter with high rainfall/low evapo-transpiration.
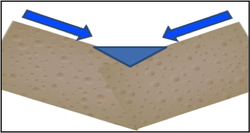
Concentrated runoff / Erosion
· Occurs where water flow converges, effectively extending the stream network into the field.
· Concentrated runoff is often connected with erosion (transfer of soil) in talwegs and tramlines
· Occurs where water flow converges, effectively extending the stream network into the field.
· Concentrated runoff is often connected with erosion (transfer of soil) in talwegs and tramlines
Mitigation measures
Mitigation measures focus on increasing infiltration &reducing soil erosion / depositing eroded soil:
· The first priority is on measures to reduce runoff / erosion at source, i.e. to keep it in the field by implementing in-field measures.
· The second priority is to prevent runoff /erosion from reaching surface water by implementing additional measures, at the edge of the field and/or in land next to the field.
· The third priority is to retain runoff / eroded soil in the catchment for some time by using retention structures to dissipate pesticide residues before entry into surface water courses.
TOPPS has proposed decision support systems (dashboards) to support the diagnosis of the pesticide runoff risks for catchments based on management at the field scale. A catalogue of measures is proposed, which allows advisors and growers to select the most appropriate risk-reduction measures compatible with productive and economically-viable farming.
Questions? Contact our project manager!
|
This project is part of the European crop protection industry’s commitment to contributing towards high quality affordable food, safeguarding water, promoting biodiversity, and protecting health. Discover more at www.hungry4change.eu
|